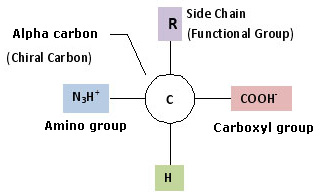
The properties of α-amino acids are complex, yet simplistic in that every molecule of an amino acid involves two functional groups: carboxyl (-COOH) and amino (-NH2).
Each molecule can contain a side chain or R group, e.g. Alanine is an example of standard amino acid containing methyl side chain group. The R groups have a variety of shapes, sizes, charges, and reactivities. This allows amino acids to be grouped according to the chemical properties of their side chains.
Table of common amino acid abbreviations and properties
|
Name |
Three letter code |
One letter code |
Molecular |
Molecular |
Residue |
Residue Weight |
pKa |
pKb |
pKx |
pl |
|
Alanine |
Ala |
A |
89.10 |
C3H7NO2 |
C3H5NO |
71.08 |
2.34 |
9.69 |
– |
6.00 |
|
Arginine |
Arg |
R |
174.20 |
C6H14N4O2 |
C6H12N4O |
156.19 |
2.17 |
9.04 |
12.48 |
10.76 |
|
Asparagine |
Asn |
N |
132.12 |
C4H8N2O3 |
C4H6N2O2 |
114.11 |
2.02 |
8.80 |
– |
5.41 |
|
Aspartic acid |
Asp |
D |
133.11 |
C4H7NO4 |
C4H5NO3 |
115.09 |
1.88 |
9.60 |
3.65 |
2.77 |
|
Cysteine |
Cys |
C |
121.16 |
C3H7NO2S |
C3H5NOS |
103.15 |
1.96 |
10.28 |
8.18 |
5.07 |
|
Glutamic acid |
Glu |
E |
147.13 |
C5H9NO4 |
C5H7NO3 |
129.12 |
2.19 |
9.67 |
4.25 |
3.22 |
|
Glutamine |
Gln |
Q |
146.15 |
C5H10N2O3 |
C5H8N2O2 |
128.13 |
2.17 |
9.13 |
– |
5.65 |
|
Glycine |
Gly |
G |
75.07 |
C2H5NO2 |
C2H3NO |
57.05 |
2.34 |
9.60 |
– |
5.97 |
|
Histidine |
His |
H |
155.16 |
C6H9N3O2 |
C6H7N3O |
137.14 |
1.82 |
9.17 |
6.00 |
7.59 |
|
Hydroxyproline |
Hyp |
O |
131.13 |
C5H9NO3 |
C5H7NO2 |
113.11 |
1.82 |
9.65 |
– |
– |
|
Isoleucine |
Ile |
I |
131.18 |
C6H13NO2 |
C6H11NO |
113.16 |
2.36 |
9.60 |
– |
6.02 |
|
Leucine |
Leu |
L |
131.18 |
C6H13NO2 |
C6H11NO |
113.16 |
2.36 |
9.60 |
– |
5.98 |
|
Lysine |
Lys |
K |
146.19 |
C6H14N2O2 |
C6H12N2O |
128.18 |
2.18 |
8.95 |
10.53 |
9.74 |
|
Methionine |
Met |
M |
149.21 |
C5H11NO2S |
C5H9NOS |
131.20 |
2.28 |
9.21 |
– |
5.74 |
|
Phenylalanine |
Phe |
F |
165.19 |
C9H11NO2 |
C9H9NO |
147.18 |
1.83 |
9.13 |
– |
5.48 |
|
Proline |
Pro |
P |
115.13 |
C5H9NO2 |
C5H7NO |
97.12 |
1.99 |
10.60 |
– |
6.30 |
|
Pyroglutamatic |
Glp |
U |
139.11 |
C5H7NO3 |
C5H5NO2 |
121.09 |
– |
– |
– |
5.68 |
|
Serine |
Ser |
S |
105.09 |
C3H7NO3 |
C3H5NO2 |
87.08 |
2.21 |
9.15 |
– |
5.68 |
|
Threonine |
Thr |
T |
119.12 |
C4H9NO3 |
C4H7NO2 |
101.11 |
2.09 |
9.10 |
– |
5.60 |
|
Tryptophan |
Trp |
W |
204.23 |
C11H12N2O2 |
C11H10N2O |
186.22 |
2.83 |
9.39 |
– |
5.89 |
|
Tyrosine |
Tyr |
Y |
181.19 |
C9H11NO3 |
C9H9NO2 |
163.18 |
2.20 |
9.11 |
10.07 |
5.66 |
|
Valine |
Val |
V |
117.15 |
C5H11NO2 |
C5H9NO |
99.13 |
2.32 |
9.62 |
– |
5.96 |
Amino acids are crystalline solids which usually are water soluble and only sparingly dissoluble in organic solvents. Their solubility depends on the size and nature of the side chain. Amino acids have very high melting points, up to 200-300°C. Their other properties varying for each particular amino acid.
Post time: Apr-19-2021





